 Home
Home
Knee Arthroscopy
(for russian and italian, scroll down)
Understanding Knee Anatomy
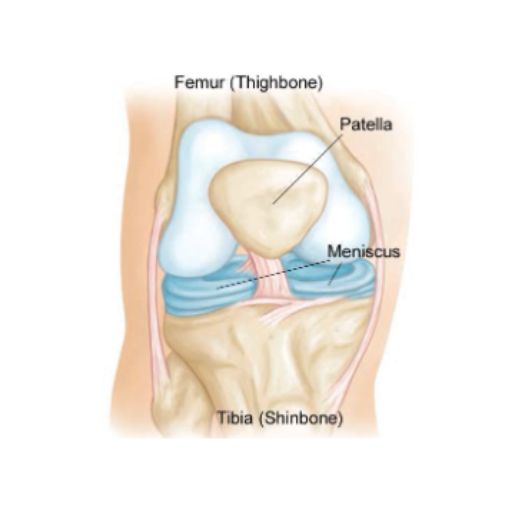
The knee is one of the most intricate and essential joints in the human body. It connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone), with the patella (kneecap) sitting at the front to protect and enhance movement. A smaller bone, the fibula, also plays a supporting role.
For smooth and pain-free motion, the knee’s surfaces are lined with articular cartilage, a slick and resilient tissue that minimizes friction. Between the femur and tibia lie the menisci, two C-shaped cartilage structures that function as shock absorbers, providing both cushioning and stability to the joint.
The knee’s integrity is maintained by ligaments—the cruciate and collateral ligaments—which prevent excessive movement and provide essential stability. Tendons connect muscles to bones, enabling motion, while the synovial membrane inside the joint capsule produces synovial fluid, ensuring smooth lubrication.
What is Knee Arthroscopy?
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat various knee conditions. Using an arthroscope—a tiny camera inserted through small incisions—the surgeon can assess the joint and perform necessary repairs without the need for large incisions.
Key Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery
- Less pain and reduced risk of complications
- Most patients return home the same day
When is Knee Arthroscopy Recommended?
Knee arthroscopy is commonly used to treat:
- Torn meniscus – A frequent cause of pain and instability.
- Torn or damaged cruciate ligament – Affects knee stability, common in athletes.
- Loose cartilage fragments – Can cause locking or catching sensations.
- Inflamed synovial tissue – May lead to chronic swelling and discomfort.
- Patellar misalignment – Causes improper tracking of the kneecap.
- Certain knee fractures – Some cases may benefit from arthroscopic management.
How is Knee Arthroscopy Performed?
1️⃣ The procedure is typically done under general anesthesia, but other options may be used depending on the patient’s condition.
2️⃣ The surgeon makes two to three small incisions around the knee.
3️⃣ Sterile saline solution is injected to expand the joint, improving visibility.
4️⃣ The arthroscope is inserted, providing a real-time view of the knee on a video monitor.
5️⃣ The surgeon assesses the damage and, if necessary, introduces specialized instruments to perform repairs.
Possible treatments include:
Meniscus repair or removal
Cruciate ligament reconstruction
Cartilage repair or removal of loose fragments
Removal of inflamed synovial tissue
Patellar realignment
Microfracture technique to stimulate cartilage regrowth
Recovery & Postoperative Care
Most patients return home the same day and can resume light activities soon after surgery.
Pain management – Medications will be prescribed as needed.
Gradual mobility – Some patients may walk without assistance, while others require crutches or braces.
Rehabilitation – A personalized physical therapy plan helps restore strength and movement.
Is Knee Arthroscopy Safe?
Yes! Knee arthroscopy is a safe and low-risk procedure. However, as with any surgery, rare complications may occur:
Bleeding inside the joint
Infection
Temporary knee stiffness
Persistent knee pain (in rare cases)
If you experience unusual swelling, fever, or severe pain, consult your doctor immediately.
Get Back to an Active Life
Knee arthroscopy is a modern, effective solution for many knee problems, allowing faster recovery and less postoperative discomfort.
Schedule your consultation today and take the first step towards pain-free movement!
Артроскопия коленного сустава
Минимально инвазивное решение для лечения проблем с коленом
Анатомия коленного сустава
Коленный сустав – один из самых сложных и важных суставов в организме человека. Он соединяет бедренную кость (фемур) и большеберцовую кость (тибия), а надколенник (пателла) защищает сустав и облегчает движение. Малоберцовая кость (фибула) также играет вспомогательную роль.
Для обеспечения плавных и безболезненных движений суставные поверхности покрыты суставным хрящом – гладкой и прочной тканью, уменьшающей трение. Между бедренной и большеберцовой костью расположены мениски – две С-образные хрящевые структуры, выполняющие амортизирующую функцию и обеспечивающие стабильность.
Крестовидные и боковые связки удерживают колено в правильном положении, предотвращая излишние движения. Сухожилия соединяют мышцы с костями, а синовиальная мембрана выделяет синовиальную жидкость, обеспечивающую смазку сустава.

Что такое артроскопия коленного сустава?
Артроскопия – это малоинвазивная хирургическая процедура, которая позволяет диагностировать и лечить повреждения колена без крупных разрезов. Используется артроскоп – миниатюрная камера, которая вводится в сустав через небольшие разрезы, позволяя хирургу точно оценить состояние колена и провести необходимые манипуляции.
Основные преимущества:
- Быстрое восстановление и минимальный дискомфорт
- Минимальные разрезы и низкий риск осложнений
- Выписка в тот же день для большинства пациентов

Когда показана артроскопия коленного сустава?
Процедура рекомендуется при следующих состояниях:
- Разрыв мениска – Одна из самых распространенных травм, вызывающая боль и нестабильность.
- Разрыв передней или задней крестообразной связки – Частая травма у спортсменов.
- Свободные хрящевые или костные фрагменты – Могут вызывать блокировку сустава.
- Воспаление синовиальной оболочки – Приводит к отеку и дискомфорту.
- Неправильное положение надколенника – Вызывает боль и ускоряет износ хряща.
- Некоторые переломы коленного сустава – В некоторых случаях можно лечить артроскопически.
Как проходит процедура?
1️⃣ Анестезия – Обычно используется общий наркоз, но возможны другие варианты.
2️⃣ Минимальные разрезы – Делается два или три небольших разреза вокруг колена.
3️⃣ Осмотр сустава – Внутрь вводится стерильный физиологический раствор для улучшения видимости.
4️⃣ Лечение повреждений – Используются специальные инструменты для устранения проблемы.
Возможные хирургические вмешательства:
Удаление или восстановление поврежденного мениска
Реконструкция крестообразных связок
Удаление фрагментов хряща или костей
Коррекция положения надколенника
Микрофрактуры для стимуляции роста хряща
Восстановление и послеоперационный уход
Постепенное восстановление подвижности – В некоторых случаях могут понадобиться костыли.
Обезболивание – Назначаются необходимые препараты.
Реабилитация – Физиотерапия помогает восстановить силу и подвижность.
Верните свободу движения без боли. Запишитесь на консультацию!
Artroscopia del Ginocchio
Una Soluzione Minimamente Invasiva per i Problemi al Ginocchio
Anatomia del Ginocchio
L’articolazione del ginocchio è una delle più complesse e importanti del corpo umano. Collega il femore (osso della coscia) alla tibia (osso della gamba), con la rotula (patella) che protegge la parte anteriore e facilita il movimento. Il perone (fibula) contribuisce alla stabilità.
Per un movimento fluido e senza dolore, le superfici ossee sono ricoperte da cartilagine articolare, un tessuto liscio e resistente che riduce l’attrito. Tra femore e tibia si trovano i menischi, due strutture a forma di C che assorbono gli urti e migliorano la stabilità.
I legamenti crociati e collaterali stabilizzano il ginocchio e prevengono movimenti eccessivi. I tendini collegano i muscoli alle ossa per consentire il movimento, mentre la membrana sinoviale lubrifica l’articolazione.

Che cos’è l’Artroscopia del Ginocchio?
L’artroscopia del ginocchio è una tecnica chirurgica minimamente invasiva che consente di diagnosticare e trattare le lesioni senza incisioni estese. Utilizza un artroscopio, una microcamera che il chirurgo introduce nell’articolazione per visualizzare e riparare i danni con precisione.
Principali vantaggi:
- Recupero rapido con meno dolore
- Cicatrici minime e basso rischio di complicazioni
- Dimissione nella stessa giornata per la maggior parte dei pazienti

Quando è indicata l’Artroscopia del Ginocchio?
Questa procedura è indicata in caso di:
- Lesione del menisco – Può causare dolore e instabilità.
- Lesione del legamento crociato – Spesso associata a traumi sportivi.
- Frammenti cartilaginei o ossei mobili – Possono bloccare il movimento.
- Infiammazione della membrana sinoviale – Causa gonfiore e disagio.
- Disallineamento della rotula – Può provocare dolore e usura anomala.
- Fratture specifiche del ginocchio – Alcuni casi possono beneficiare della chirurgia artroscopica.
Come si svolge l’Artroscopia?
1️⃣ Anestesia – Solitamente generale, ma può essere adattata al paziente.
2️⃣ Incisioni minime – Due o tre piccole incisioni vengono effettuate attorno al ginocchio.
3️⃣ Visualizzazione interna – Viene iniettata una soluzione salina sterile per ampliare lo spazio articolare.
4️⃣ Riparazione dei danni – Il chirurgo utilizza strumenti specializzati per eseguire il trattamento necessario.
Possibili interventi includono:
Riparazione o rimozione del menisco danneggiato
Ricostruzione dei legamenti crociati
Rimozione di frammenti ossei o cartilaginei mobili
Allineamento della rotula
Tecniche di stimolazione della crescita cartilaginea (microfratture)
Microfracture technique to stimulate cartilage regrowth
Recupero e Cura Postoperatoria
Movimento progressivo – Potrebbe essere necessario l’uso di stampelle o un tutore.
Controllo del dolore – Verranno prescritti farmaci antidolorifici, se necessario.
Riabilitazione – La fisioterapia aiuta a rafforzare il ginocchio e ripristinare la mobilità.
Rehabilitation – A personalized physical therapy plan helps restore strength and movement.
Ritorna a muoverti senza dolore. Prenota oggi una consulenza!

